Introduction:
Oral health issues can range from common dental problems to more specific conditions. One such condition is a mucocele, which is a type of cyst that commonly appears in the mouth. While mucoceles are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort and affect your oral health if left untreated. In this article, we will explore what mucoceles are, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is a Mucocele?
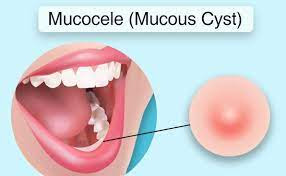
A mucocele, also known as a mucous cyst, is a benign and painless cyst that forms when a salivary gland duct gets blocked or damaged. The salivary glands produce saliva, which helps in digestion and oral hygiene. When the ducts become blocked or ruptured, saliva accumulates and forms a cyst. Mucoceles are typically small, round-shaped, and filled with clear fluid. They are most commonly found in the lower lip, but can also occur on the tongue, inner cheek, or the roof of the mouth.
Causes of Mucoceles:

The exact causes of mucoceles are not always clear. However, several factors can contribute to their formation, including:
1. Trauma:
Accidental biting, sucking on the lip, or any form of oral trauma can damage the salivary gland ducts, leading to mucocele formation.
2. Blockage:
Blockage or obstruction of the salivary gland ducts can occur due to mucus buildup or damage to the gland.
3. Chronic Irritation:
Constant irritation from activities like tongue thrusting, lip sucking, or wearing ill-fitting oral appliances can contribute to the development of mucoceles.
Is Mucocele Harmful?
In general, mucoceles are harmless and painless. However, they can cause discomfort, especially if they are large in size or get accidentally bitten. Mucoceles can interfere with speaking, eating, and oral hygiene practices. If left untreated, they may become infected, leading to inflammation and pain.

Symptoms of Mucoceles:
The most common symptoms of mucoceles include:
- A soft, fluid-filled swelling or bump in the mouth, usually on the lower lip.
- Bluish or transparent appearance due to the accumulation of clear fluid.
- Discomfort or pain if the mucocele gets traumatized or bitten.
- Difficulty in speaking or eating, particularly if the mucocele is large in size.
Treatment Options for Mucoceles:
Small mucoceles often resolve on their own within a few weeks or months. However, if the cyst persists or causes discomfort, medical intervention may be necessary. Here are some common treatment options for mucoceles:
1. Observation:
In many cases, your dentist or oral surgeon may suggest monitoring the mucocele to see if it resolves spontaneously. They may advise avoiding trauma or irritation to the area and practicing good oral hygiene.
2. Surgical Removal:
If the mucocele is large, causing persistent discomfort, or not resolving on its own, surgical removal may be recommended. The procedure involves removing the cyst and repairing the damaged ducts or glands to prevent recurrence.
3. Laser Treatment:
Some mucoceles can be treated using laser therapy. This minimally invasive procedure involves using a laser to vaporize the cyst and seal the affected ducts.
4. Cryosurgery:
Freezing the mucocele with liquid nitrogen can be an effective treatment option. Cryosurgery helps to destroy the cyst and promote healing.
Conclusion:
Mucoceles are common oral cysts that can cause discomfort and interfere with daily activities. While generally harmless, they should be evaluated by a dental professional if they persist or cause significant discomfort. Treatment options may include observation, surgical removal, laser therapy, or cryosurgery, depending on the size, location, and severity of the mucocele.
If you suspect the presence of a mucocele or experience any oral abnormalities, it is advisable to seek professional dental care for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
